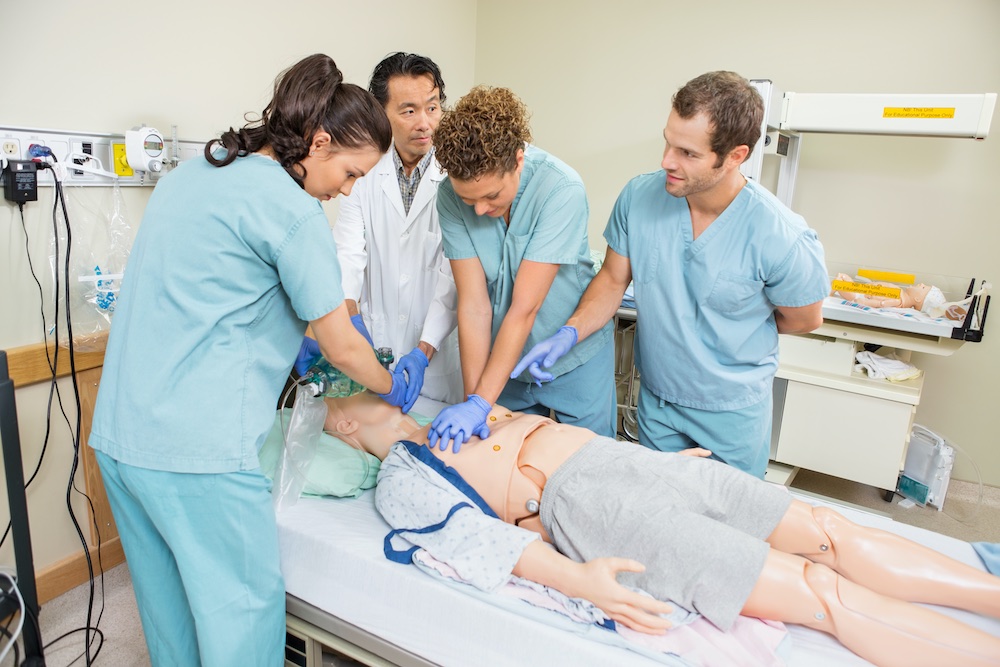
Effective interpersonal communication is essential for healthcare providers. It impacts patient satisfaction, adherence to treatment plans, and overall health outcomes. Medical simulation training has become a vital tool for developing these skills, offering realistic, hands-on experiences that prepare healthcare professionals for real-life interactions. This blog post explores how simulation training enhances interpersonal communication skills, highlighting advanced techniques and benefits that are often overlooked.
The importance of interpersonal skills in healthcare
Interpersonal skills in healthcare include empathy, active listening, clear communication, and the ability to provide support and comfort to patients. These skills are crucial for building trust, ensuring patient compliance, and improving the quality of care. According to a study published in the journal of general internal medicine, effective communication can lead to a 19% increase in patient adherence to treatment plans.
How simulation training enhances interpersonal skills
Realistic patient interactions
Simulation training uses standardized patients (actors trained to portray specific medical conditions and emotional states) to create realistic patient interactions. These scenarios allow healthcare providers to practice and refine their communication skills in a controlled environment.
Example: trainees might engage in a simulation where they must deliver bad news to a patient. This scenario helps them develop the ability to communicate sensitively and empathetically, a crucial skill in healthcare.
A study by the association of american medical colleges (aamc) found that students who participated in standardized patient simulations showed a 28% improvement in their interpersonal communication skills.
Advanced techniques in simulation training
Role-playing and scenario-based training
Role-playing and scenario-based training are fundamental components of simulation that help healthcare providers practice interpersonal skills in various clinical situations. These techniques provide opportunities to handle difficult conversations, manage patient emotions, and collaborate with colleagues.
Example: a role-playing scenario might involve a patient expressing frustration or fear about their treatment. Healthcare providers must use active listening and empathy to address the patient’s concerns effectively.
The journal of medical education reported that role-playing exercises improved communication skills by 32% compared to traditional lecture-based learning.
Virtual reality (vr) and augmented reality (ar)
Vr and ar technologies offer immersive experiences that enhance the realism of simulation training. These technologies can simulate complex clinical environments and patient interactions, providing a deeper level of engagement and learning.
Example: using vr, healthcare providers can enter a virtual clinic where they interact with virtual patients displaying various emotional states and medical conditions. This immersive experience helps them practice and refine their communication skills in a lifelike setting.
Research by the american medical association (ama) indicates that vr-based training improved healthcare providers’ confidence and competence in interpersonal communication by 25%.
Continuous feedback and assessment
One of the key benefits of simulation training is the ability to provide continuous feedback and assessment. After each simulation, participants receive detailed feedback on their performance, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement.
Debriefing sessions
Debriefing sessions are a critical part of simulation training. These sessions involve reviewing the simulation exercise, discussing what went well, and identifying opportunities for improvement. This reflective practice helps healthcare providers internalize lessons and enhance their communication skills.
Example: after a simulation involving a difficult patient interaction, participants might discuss how they handled the situation, what they could have done differently, and how they can apply these insights to future interactions.
The journal of clinical nursing found that debriefing sessions led to a 30% improvement in communication skills among nursing students.
Building empathy and emotional intelligence
Simulation training also focuses on building empathy and emotional intelligence, essential components of effective interpersonal communication. By experiencing various patient perspectives and emotions, healthcare providers can develop a deeper understanding and ability to connect with patients.
Example: simulations that involve role-playing as a patient can help healthcare providers gain insights into the patient experience, fostering empathy and compassion.
A study published in the journal of health communication highlighted that empathy training through simulations increased healthcare providers’ empathy levels by 22%.
Conclusion
Medical simulation training is a powerful tool for enhancing interpersonal communication skills among healthcare providers. By offering realistic patient interactions, continuous feedback, advanced techniques such as vr and ar, and a focus on empathy, simulations provide comprehensive training that goes beyond traditional methods. These benefits lead to improved patient satisfaction, better adherence to treatment plans, and overall enhanced quality of care. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the role of simulation training in developing interpersonal skills will become increasingly vital.